How to Leverage Technology for Quality Assurance and Compliance

Data Control for Quality Assurance
Data collection and statistical process control (SPC) are key components of a successful quality assurance program. Quality managers must have a clear understanding of how to collect, process, and analyze data in order to ensure that products are consistently produced to the highest standards of quality. This article provides an overview of how data collection and SPC can be used to ensure quality assurance.
Data Collection
Data collection is essential to any quality assurance program. Quality managers must be able to accurately collect data in order to identify potential issues, measure performance, and ensure that the product meets quality standards. Quality managers must also be aware of the different types of data available and how to collect it. This includes both quantitative and qualitative data. The following is a description of the two main types of data collection methods.
Manual Data Collection
Manual data collection is one of the most common methods used in quality control. This approach involves manually entering data into a spreadsheet or other software program, such as a defect tracking system. Manual data collection is most often used when a limited number of items need to be inspected, or when the data being collected is relatively simple. This approach can be time-consuming, but it’s typically the most cost-effective option.

One of the key benefits of manual data collection is that it allows for greater flexibility in terms of the type of data that can be collected. With manual data collection, quality control teams can collect detailed information on any aspect of the product or process, as well as custom data points that may not be available in an automated system.
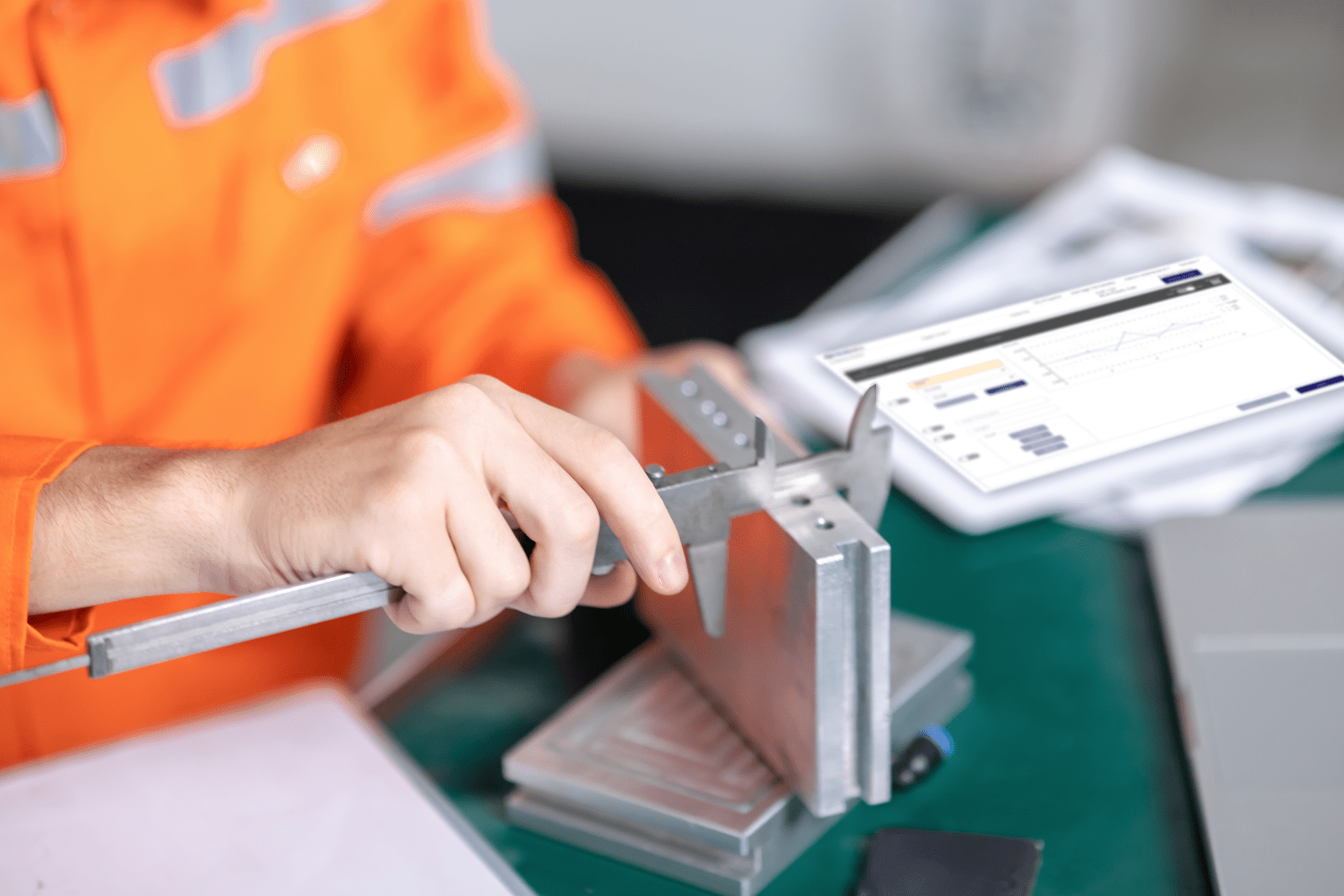
Automated Data Collection
Automated data collection is a more advanced approach to data collection in quality control. This approach typically involves the use of specialized equipment, such as sensors, scanners, or other devices, to capture data points in real time. Automated data collection can be used for large-scale inspections and is particularly useful when collecting large amounts of data or data points that are difficult to capture manually.
One of the key advantages of automated data collection is its accuracy. Automated systems can be configured to capture specific data points that may be difficult or impossible to capture manually. This can result in more accurate data and fewer errors, which can help improve the overall quality of the product or process.
Statistical Process Control
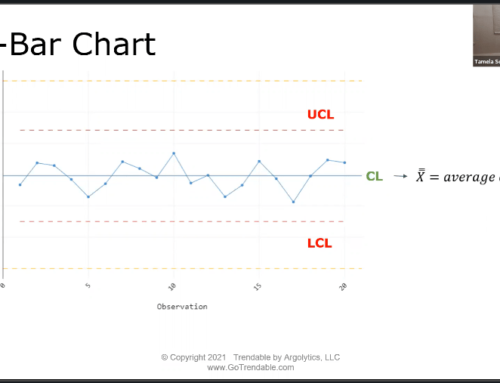
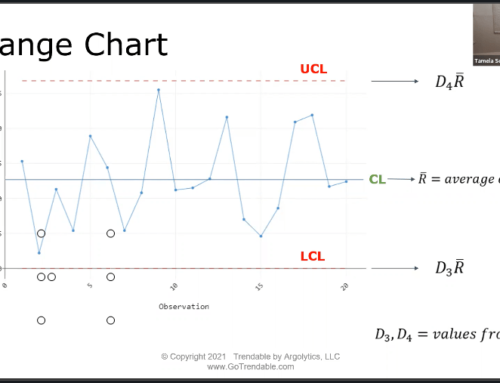
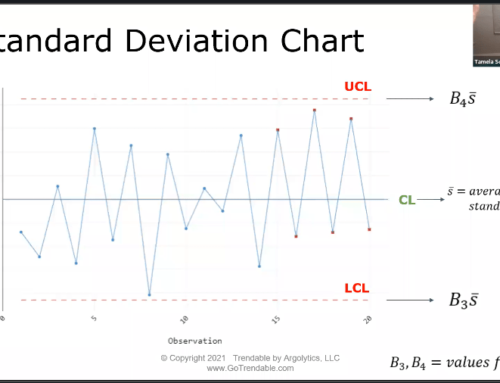
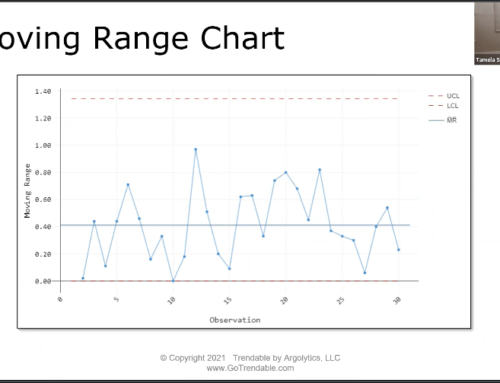
Once the data has been collected, it must be processed and analyzed. This is where statistical process control (SPC) comes in. SPC is a method of analyzing data to identify and address problems in quality assurance. It is used to monitor products and processes in order to ensure that they are consistently meeting quality standards.
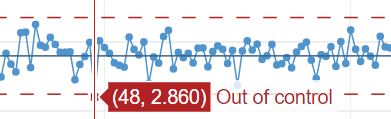
SPC involves the use of statistical and graphical methods to identify trends and patterns in data that may indicate a potential problem. Quality managers must be aware of the different SPC methods available and how to use them to identify and address quality assurance issues. They must also be aware of how to interpret the results of SPC to ensure that products and processes are consistently meeting quality standards.
Data Analysis Tools
Data analysis tools are a type of software that can be used to analyze data collected in quality control. These tools can be used to evaluate data points, identify trends, and compare performance over time. Data analysis tools can also be used to generate custom reports that can be used to assess the effectiveness of quality control processes.
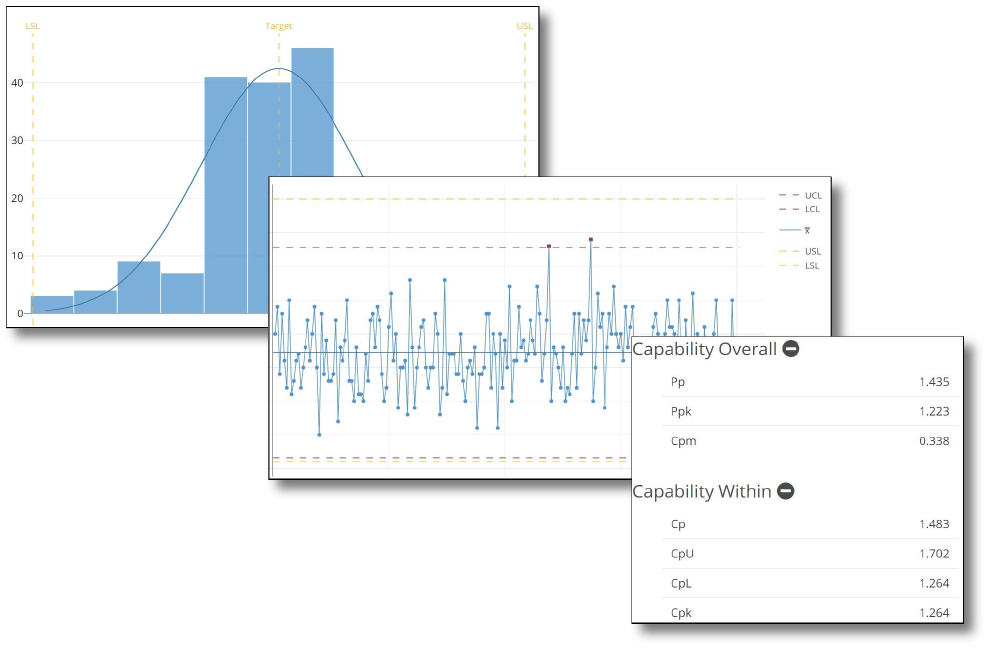
Data analysis tools can be used in conjunction with both manual and automated data collection. By combining data analysis with data collection, quality control teams can quickly identify potential issues and areas for improvement, as well as track performance over time.
Defect Reporting
Defect reporting is the process of tracking any issues or discrepancies that occur in the manufacturing process. This includes noting errors in the production line, defects in the raw materials, or any other issues that would result in a lower quality product. By keeping track of defects, quality managers can identify areas of improvement and develop strategies to ensure that products meet their quality standards.
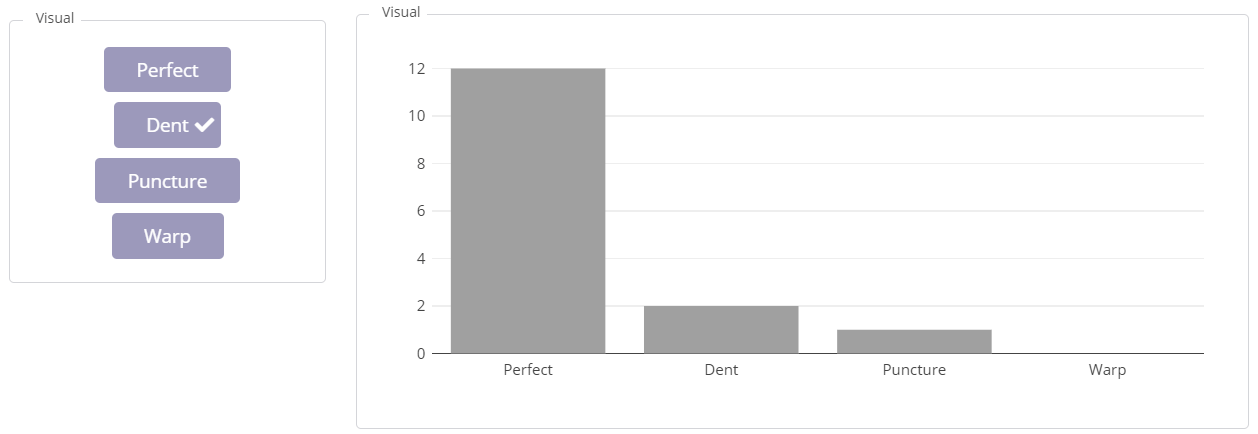
Having an effective defect reporting system in place can help to reduce the risk of defective products reaching the consumer. It also enables quality managers to identify any issues early on, so they can take corrective action before the problem escalates.
Key Takeaways
Data collection and statistical process control are essential components of a successful quality assurance program. Quality managers must have a clear understanding of how to collect, process, and analyze data in order to ensure that products are consistently produced to the highest standards of quality. Quality managers must also be aware of the importance of accurate data collection, the different methods of data collection, and the different SPC methods available. They must also have a clear understanding of how to implement data collection and SPC, as well as how to train and educate employees on them. By understanding and implementing data collection and SPC, quality managers can ensure that products and processes meet quality standards.
If you want to ensure that your quality assurance program is successful, it is essential to have a clear understanding of data collection and statistical process control. By taking the time to learn about how to collect and analyze data, you can ensure that your products and processes meet the highest standards of quality.